RMBS Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities A Comprehensive Guide
Rmbs residential mortgage backed securities – RMBS Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities represent a significant segment of the financial market, offering investors the opportunity to participate in the mortgage market through a diversified investment vehicle. RMBS are created through a process called securitization, where a pool of mortgages is packaged into bonds and sold to investors. These bonds, in turn, generate income based on the underlying mortgage payments.
The concept of securitization has revolutionized the mortgage market, allowing for the efficient transfer of risk and liquidity. This process has enabled a broader range of investors to participate in the mortgage market, leading to increased competition and lower borrowing costs for homeowners. This guide delves into the intricacies of RMBS, exploring their structure, types, risk considerations, market dynamics, and investment strategies.
Introduction to RMBS (Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities)
Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities (RMBS) are a type of asset-backed security that is backed by a pool of residential mortgages. They are a key component of the global financial market, providing investors with a way to invest in the housing market.
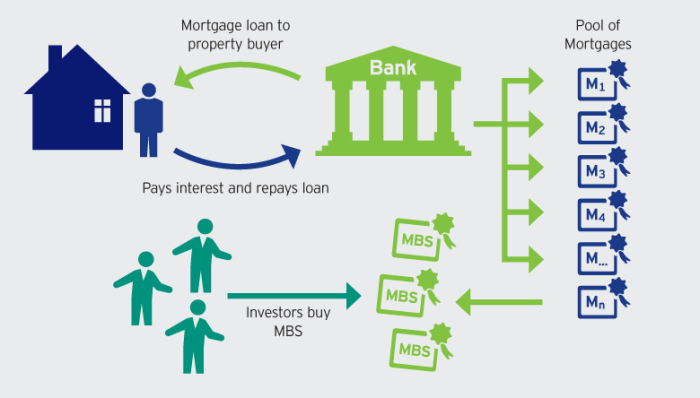
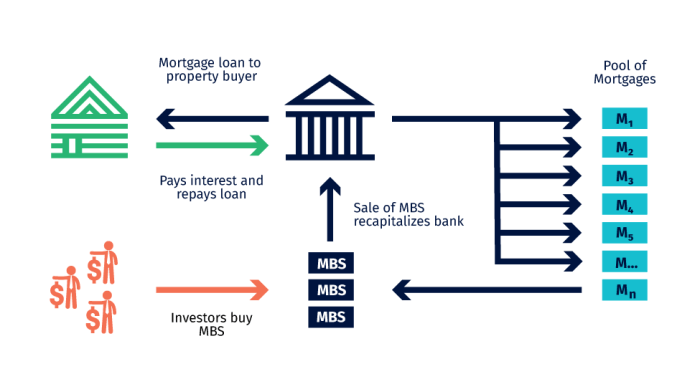
RMBS are created through a process called securitization, which involves packaging a group of mortgages into a single security. This process allows investors to purchase a piece of a diversified pool of mortgages, rather than investing in individual loans.
Securitization Process
The process of securitization begins with a group of mortgages being originated by lenders, such as banks or mortgage companies. These mortgages are then pooled together and sold to a special purpose entity (SPE). The SPE issues RMBS to investors, which represent ownership in the underlying pool of mortgages. The SPE then uses the proceeds from the sale of the RMBS to purchase the mortgages from the originators.
The SPE then collects the mortgage payments from the borrowers and distributes these payments to the RMBS investors, according to the terms of the security. This process allows investors to receive regular interest payments from the mortgages, as well as the principal repayment when the mortgages mature.
Historical Overview of RMBS
RMBS have been around for decades, with the first RMBS being issued in the 1970s. The market for RMBS grew significantly in the 1980s and 1990s, as investors sought out new ways to invest in the housing market.
The growth of the RMBS market was fueled by a number of factors, including:
- The increasing availability of mortgages
- The development of new securitization techniques
- The growth of the institutional investor market
However, the RMBS market also experienced a period of significant turmoil during the financial crisis of 2008. The crisis was triggered by a sharp decline in housing prices, which led to a surge in mortgage defaults. This resulted in significant losses for investors who held RMBS, as the value of these securities plummeted.
Despite the challenges of the financial crisis, the RMBS market has since recovered and continues to play an important role in the global financial market.
Risk and Return Considerations

Investing in RMBS involves a complex interplay of risk and return, making it crucial to understand the potential pitfalls and rewards. Investors need to carefully weigh the various factors influencing the performance of these securities, including interest rate fluctuations, credit quality of underlying mortgages, and prepayment behavior.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is a major concern for RMBS investors. As interest rates rise, the value of existing fixed-income securities, including RMBS, declines. This is because investors can now earn a higher return on newly issued bonds with higher interest rates, making older bonds less attractive.
- Example: Consider a RMBS issued with a fixed coupon rate of 5%. If market interest rates increase to 6%, investors would prefer to buy newly issued bonds offering a 6% return. This would drive down the price of the existing RMBS with a 5% coupon to make its yield competitive.
Credit Risk
RMBS are backed by a pool of mortgages, and the creditworthiness of the borrowers plays a crucial role in determining the overall risk of the security. If borrowers default on their mortgage payments, it can lead to losses for RMBS investors.
- Example: If a significant number of borrowers in a mortgage pool experience financial hardship and default on their loans, the value of the RMBS could decline as the cash flows from the underlying mortgages are reduced.
Prepayment Risk
Prepayment risk arises from the possibility of borrowers repaying their mortgages earlier than expected, which can disrupt the expected cash flows from the RMBS. Prepayments can occur due to various reasons, such as refinancing at lower interest rates, selling the property, or paying off the mortgage early.
- Example: If interest rates fall, borrowers may refinance their mortgages at lower rates, leading to prepayments that reduce the principal balance of the RMBS and shorten the duration of the investment.
Return on RMBS
The return on RMBS is influenced by a combination of factors, including:
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates generally lead to lower RMBS prices, but they also offer higher coupon payments.
- Credit Quality of Underlying Mortgages: RMBS backed by higher-quality mortgages (e.g., prime mortgages) tend to have lower credit risk and offer lower yields. RMBS backed by lower-quality mortgages (e.g., subprime mortgages) carry higher credit risk and offer higher yields to compensate for the potential for higher defaults.
- Prepayment Rates: Higher prepayment rates can reduce the duration of the investment and potentially lower the overall return.
Risk-Return Profiles of RMBS Tranches, Rmbs residential mortgage backed securities
RMBS are often structured into different tranches, each with a distinct risk-return profile.
- Senior Tranches: Senior tranches have the highest priority for receiving principal and interest payments and typically offer lower yields. They are considered less risky due to their higher position in the payment structure.
- Junior Tranches: Junior tranches have lower priority for receiving payments and typically offer higher yields to compensate for their higher risk. They are more vulnerable to losses in case of defaults or prepayments.
Investment Strategies: Rmbs Residential Mortgage Backed Securities

Investing in RMBS involves a careful consideration of risk tolerance and investment objectives. Different strategies can be employed to achieve specific financial goals, and understanding the nuances of RMBS is crucial for successful investment.
Risk Tolerance and Investment Objectives
The first step in developing an RMBS investment strategy is to assess your risk tolerance and investment objectives. This involves understanding your ability to handle potential losses and the timeframe for achieving your financial goals. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may be willing to accept greater volatility in exchange for potentially higher returns. On the other hand, those with a lower risk tolerance may prefer investments with lower volatility, even if it means lower returns.
- Income Generation: Investors seeking regular income may choose RMBS with a high coupon rate, offering consistent interest payments. These securities often have a lower risk profile compared to higher-yielding bonds, providing a stable stream of income.
- Capital Preservation: Investors prioritizing capital preservation may prefer RMBS with a lower coupon rate and a shorter maturity. These securities offer a lower risk of principal loss, making them suitable for conservative investors.
- Growth Potential: For investors seeking growth potential, RMBS with a longer maturity and a higher coupon rate may be considered. These securities offer the potential for higher returns, but also carry a higher risk of principal loss.
RMBS in Diversified Portfolios
RMBS can play a valuable role in diversified investment portfolios, offering potential benefits like income generation, capital preservation, and diversification. By incorporating RMBS into a portfolio, investors can potentially enhance returns while mitigating risk.
- Diversification: RMBS can provide diversification benefits by offering exposure to the real estate market, which is often less correlated with other asset classes like stocks and bonds. This can help to reduce overall portfolio volatility and enhance risk-adjusted returns.
- Income Generation: RMBS can generate regular income through coupon payments, providing a stable stream of cash flow for investors.
- Capital Preservation: Depending on the specific RMBS chosen, investors can potentially preserve capital by investing in securities with a lower risk profile.
Investment Scenarios
Here are some specific examples of how RMBS can be used in different investment scenarios:
Income Generation
An investor seeking a stable stream of income could invest in RMBS with a high coupon rate. For instance, a senior RMBS tranche with a 5% coupon rate could provide a consistent income stream. This strategy is suitable for investors with a lower risk tolerance and a need for regular income.
Capital Preservation
An investor seeking to preserve capital could invest in RMBS with a lower coupon rate and a shorter maturity. For example, a junior RMBS tranche with a 3% coupon rate and a 5-year maturity could offer a lower risk of principal loss. This strategy is suitable for conservative investors who prioritize capital preservation over potential growth.
Growth Potential
An investor seeking growth potential could invest in RMBS with a longer maturity and a higher coupon rate. For example, a senior RMBS tranche with a 6% coupon rate and a 10-year maturity could offer the potential for higher returns. However, this strategy carries a higher risk of principal loss and is suitable for investors with a higher risk tolerance.
Understanding the complexities of RMBS is essential for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and potentially enhance returns. From comprehending the various types of RMBS and their associated risks to navigating the evolving regulatory landscape, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of this important investment instrument. By grasping the fundamental principles of RMBS, investors can make informed decisions and potentially capitalize on the opportunities presented by this dynamic market.
Clarifying Questions
What are the benefits of investing in RMBS?
Investing in RMBS can provide investors with potential benefits such as diversification, income generation, and exposure to the mortgage market.
How can I assess the risk of investing in RMBS?
Understanding the various types of RMBS, their associated risks, and the credit quality of the underlying mortgages is crucial for assessing the risk of investing in RMBS.
What are the potential risks associated with investing in RMBS?
Risks associated with investing in RMBS include interest rate risk, credit risk, and prepayment risk.
How does the regulatory environment impact RMBS?
Regulatory changes can significantly impact the issuance, trading, and pricing of RMBS.
RMBS, or Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities, are complex financial instruments that bundle together a pool of home loans. Understanding these securities requires a solid grasp of finance, and an MBA can provide the necessary knowledge and skills. If you’re interested in pursuing a career in finance and want to learn about RMBS, consider exploring the cheapest MBA online program options available.
An MBA can equip you with the analytical tools and financial acumen needed to navigate the intricacies of RMBS and other complex financial products.
RMBS, or Residential Mortgage Backed Securities, are complex financial instruments that bundle together home loans, offering investors a piece of the mortgage market. Understanding the intricacies of these securities often requires a strong foundation in finance, which is where an MBA comes in. If you’re interested in pursuing a career in this field, you can find information about the cost of an online MBA here.
An MBA can provide the necessary analytical skills to navigate the complexities of RMBS and other financial markets.
Residential Mortgage Backed Securities (RMBS) are complex financial instruments, and understanding their intricacies can be crucial for those seeking careers in finance. An MBA can provide a solid foundation in financial analysis and risk management, and the UNC Online MBA program offers a flexible and rigorous curriculum that can equip students with the skills necessary to navigate the world of RMBS and other financial markets.
With a strong understanding of financial principles, individuals can better assess the risks and opportunities associated with these securities.
RMBS, or Residential Mortgage Backed Securities, are complex financial instruments that bundle together home mortgages. Understanding the intricacies of these securities requires a strong foundation in finance, which can be gained through an online MBA finance degree. This type of program equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to analyze and evaluate the risks associated with RMBS investments, making them more informed decision-makers in the financial world.