DTI for Investment Property A Guide to Financing
DTI for investment property plays a crucial role in determining your eligibility for financing and the terms you receive. Understanding this metric is essential for investors seeking to acquire rental properties, as it directly impacts your ability to secure a loan and ultimately, the profitability of your investment.
This guide delves into the intricacies of DTI, examining its calculation, influence on loan approval, and strategies for improving your score. We will explore how DTI impacts loan terms, cash flow, and the overall performance of your investment property. Additionally, we will address regional variations in regulations and offer insights into navigating the complexities of investment property financing.
Understanding DTI for Investment Properties
Debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a crucial metric that lenders use to assess your ability to repay a loan. It represents the percentage of your gross monthly income that goes towards your monthly debt payments. While DTI is important for both primary residences and investment properties, there are some key differences in how it’s calculated and what lenders consider.
DTI Calculation for Investment Properties
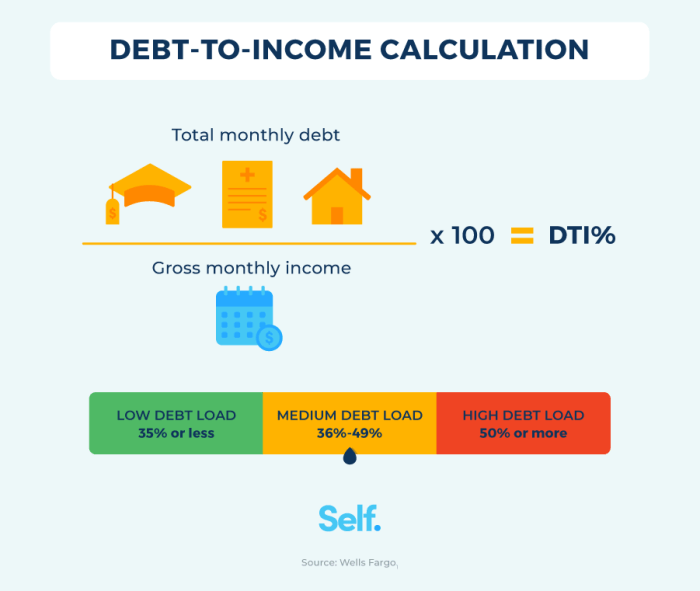
The DTI calculation for investment properties differs from that of primary residences. While the basic formula remains the same, lenders typically consider only the income and expenses related to the investment property. This means that your personal income and expenses, such as your salary and credit card payments, are not factored into the calculation.
DTI = Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income
For investment properties, your gross monthly income will be the estimated rental income from the property. Your total monthly debt payments will include the mortgage payment, property taxes, insurance, and any other expenses associated with the property.
Factors Lenders Consider When Evaluating DTI for Investment Property Loans
Lenders consider several factors when evaluating your DTI for an investment property loan. These factors include:
- Credit Score: A good credit score is essential for securing a loan, especially for investment properties. A higher credit score generally translates to lower interest rates and better loan terms.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: Lenders typically prefer a DTI below 45% for investment properties. However, this can vary depending on the lender and the specific loan program.
- Rental Income: The rental income from the property is a crucial factor in determining your DTI. Lenders want to ensure that the rental income is sufficient to cover the mortgage payments and other expenses.
- Property Value: The value of the investment property is also considered. Lenders want to make sure that the property is worth enough to cover the loan amount in case of default.
- Down Payment: Lenders may require a larger down payment for investment properties compared to primary residences. This is because investment properties are considered riskier due to the potential for fluctuations in rental income.
- Investment Experience: Lenders may also consider your experience as an investor. If you have a history of successful investment properties, it may improve your chances of securing a loan.
Impact of DTI on Investment Property Financing
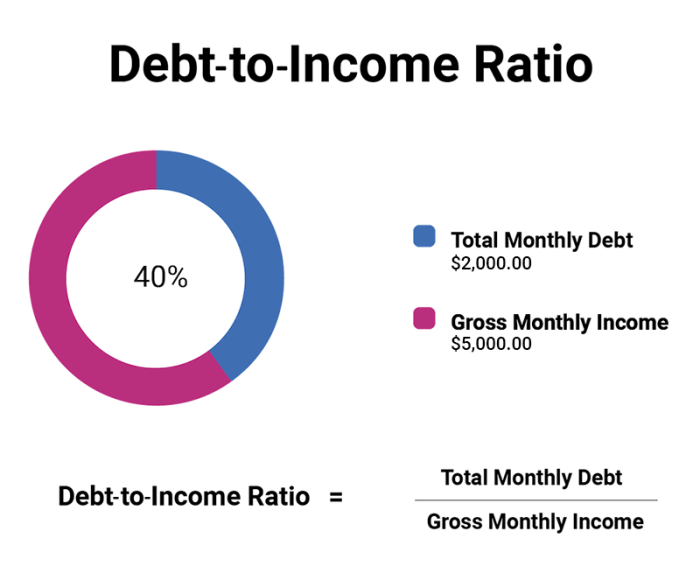
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a crucial factor lenders consider when assessing your ability to repay an investment property loan. It’s a ratio that compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. A higher DTI generally indicates a greater financial burden, which can affect your loan approval and the terms offered.
Impact of DTI on Loan Approval
Your DTI plays a significant role in determining whether your loan application for an investment property will be approved. Lenders generally prefer borrowers with lower DTIs as it indicates a greater ability to manage debt obligations. If your DTI is too high, lenders may perceive you as a higher risk borrower, making them less likely to approve your loan application.
Impact of DTI on Loan Terms
A higher DTI can influence the loan terms offered, such as interest rates and loan-to-value (LTV) ratios.
Interest Rates
Lenders may offer higher interest rates to borrowers with higher DTIs. This is because they perceive a greater risk of default, so they charge a higher interest rate to compensate for that risk. For example, a borrower with a DTI of 40% may be offered an interest rate of 5.5%, while a borrower with a DTI of 30% might receive an interest rate of 5%.
Loan-to-Value Ratio
A higher DTI may also lead to a lower LTV ratio. This means you’ll be required to make a larger down payment on the property. Lenders may limit the amount they’re willing to lend to borrowers with higher DTIs to mitigate their risk. For instance, a borrower with a DTI of 40% might be offered an LTV of 75%, requiring a 25% down payment, while a borrower with a DTI of 30% might receive an LTV of 80%, requiring a 20% down payment.
Scenarios with Lower DTI
A lower DTI can often lead to more favorable loan terms, such as lower interest rates and higher LTV ratios. This is because lenders perceive borrowers with lower DTIs as having a lower risk of default.
Example 1: Lower Interest Rate
Imagine two borrowers are applying for a loan on an investment property. Borrower A has a DTI of 35% and is offered an interest rate of 4.5%. Borrower B has a DTI of 25% and is offered an interest rate of 4%. This scenario illustrates how a lower DTI can lead to a lower interest rate, saving the borrower money on interest payments over the life of the loan.
Example 2: Higher LTV Ratio
Consider two borrowers applying for a loan on a $500,000 investment property. Borrower A has a DTI of 40% and is offered an LTV of 70%, requiring a $150,000 down payment. Borrower B has a DTI of 30% and is offered an LTV of 80%, requiring a $100,000 down payment. This example shows how a lower DTI can result in a higher LTV ratio, allowing the borrower to make a smaller down payment and potentially access more financing.
Strategies for Improving DTI for Investment Properties
Improving your DTI is crucial for securing financing for investment properties. A higher DTI can indicate a greater financial risk to lenders, making it challenging to qualify for loans. Fortunately, several strategies can help you improve your DTI and increase your chances of getting approved for financing.
Increasing Income
Increasing your income can significantly boost your DTI. This can be achieved through various means, such as:
- Seeking a promotion or raise: If you’re currently employed, consider discussing your salary expectations with your employer. Highlighting your contributions and value to the company can increase your chances of receiving a raise.
- Taking on a second job: A part-time job or freelance work can supplement your income and improve your DTI. Choose a job that aligns with your skills and interests to make it more sustainable and enjoyable.
- Investing in additional income streams: Explore passive income opportunities like starting a blog, creating online courses, or investing in dividend-paying stocks. While these options might take time to generate substantial income, they can contribute to a long-term increase in your DTI.
Reducing Debt
Reducing your debt is another effective strategy for improving your DTI. This can be achieved by:
- Consolidating high-interest debt: Consolidating high-interest debt into a lower-interest loan can significantly reduce your monthly payments and free up cash flow. This can help improve your DTI and reduce your overall debt burden.
- Paying off debt faster: Make extra payments on your debt to accelerate the repayment process. Even small additional payments can significantly impact the overall interest paid and reduce the debt faster.
- Negotiating lower interest rates: Contact your lenders to discuss lowering your interest rates. By demonstrating a good payment history and credit score, you might be able to negotiate better terms and reduce your monthly payments.
Optimizing Expenses
Optimizing your expenses can free up cash flow and improve your DTI. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Creating a detailed budget: Tracking your expenses and identifying areas for savings can help you make informed financial decisions. A budget can help you prioritize essential spending and reduce unnecessary expenses.
- Negotiating lower bills: Contact your service providers, such as cable, internet, and phone companies, to negotiate lower rates or explore alternative options.
- Reducing unnecessary subscriptions: Review your subscriptions and cancel those you no longer use. This can free up significant funds and improve your DTI.
Maximizing Rental Income
Maximizing rental income is crucial for investment property success. Here are some tips:
- Conducting thorough market research: Understanding local rental market trends and analyzing comparable properties can help you set competitive and realistic rental rates.
- Offering desirable amenities: Providing attractive amenities, such as in-unit laundry, parking, or a community pool, can attract tenants and justify higher rental rates.
- Maintaining a positive tenant relationship: Building a good relationship with your tenants can encourage them to stay longer, reducing vacancy costs and ensuring consistent rental income.
Minimizing Expenses, Dti for investment property
Minimizing expenses associated with investment properties is essential for maximizing profitability. Here are some tips:
- Negotiating favorable contracts: Secure competitive rates from contractors, vendors, and service providers for maintenance, repairs, and property management.
- Implementing energy-efficient upgrades: Installing energy-efficient appliances and fixtures can reduce utility costs and increase your property’s value.
- Seeking tax deductions: Take advantage of tax deductions related to your investment property, such as depreciation, mortgage interest, and property taxes.
DTI and Investment Property Performance

DTI, or debt-to-income ratio, is a crucial metric for lenders assessing your ability to manage an investment property. However, it’s not just about securing financing; DTI directly impacts the financial performance of your investment. Understanding this relationship is vital for maximizing returns and minimizing risk.
Impact of DTI on Investment Property Profitability
DTI influences several key aspects of investment property performance, including cash flow, return on investment, and potential risks.
- Cash Flow: A higher DTI generally means a larger mortgage payment, leaving less cash flow available for other expenses and potential profits. For example, a higher DTI might limit your ability to cover maintenance costs, property taxes, or insurance premiums, potentially leading to negative cash flow.
- Return on Investment (ROI): A lower DTI often translates to a higher ROI. This is because you’re able to invest a larger portion of your income into the property, potentially leading to faster appreciation and greater returns. A higher DTI can reduce your overall investment, limiting potential profits.
- Potential Risks: A high DTI increases financial strain and vulnerability to economic fluctuations. For instance, if interest rates rise or your income decreases, a higher DTI could make it difficult to meet mortgage payments, leading to potential foreclosure.
DTI Scenarios and Investment Property Performance
The following table illustrates how different DTI scenarios can impact key investment property performance metrics:
| DTI | Cash Flow | ROI | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (e.g., 30%) | Higher | Higher | Lower |
| Moderate (e.g., 40%) | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| High (e.g., 50%) | Lower | Lower | Higher |
Note: These are general examples, and actual outcomes can vary based on individual circumstances, property type, and market conditions.
Navigating the world of investment property financing requires a comprehensive understanding of DTI. By carefully managing your debt-to-income ratio, you can optimize your chances of securing favorable loan terms, maximizing your investment’s profitability, and achieving your financial goals. Remember, a well-planned approach to DTI can be the key to unlocking the potential of your investment property portfolio.
FAQ Summary: Dti For Investment Property
What is a good DTI for investment property loans?
Lenders typically prefer a DTI below 45% for investment properties, but the ideal ratio may vary based on factors like your credit score, income, and the property type.
Can I improve my DTI for investment property financing?
Yes, you can improve your DTI by increasing your income, reducing debt, or optimizing your expenses. Consider strategies like boosting rental income, consolidating debt, or negotiating lower interest rates.
How does DTI impact my investment property’s profitability?
A higher DTI often leads to higher interest rates and lower loan-to-value ratios, potentially reducing your cash flow and return on investment. A lower DTI can improve your loan terms and enhance your investment’s profitability.
What are the regulations surrounding DTI for investment properties?
DTI requirements for investment properties can vary depending on local regulations and lending institutions. It’s essential to research the specific guidelines in your region and consult with a qualified mortgage lender.
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a crucial factor when considering an investment property, as lenders use it to assess your ability to manage additional debt. While your DTI might limit your options, there are always exciting investment opportunities near me to explore. By carefully evaluating your financial situation and researching available options, you can find a property that aligns with your DTI and investment goals.
Determining your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is crucial when considering an investment property, as it directly impacts your ability to secure financing. You might find helpful resources from Matthews Real Estate Investment Services , who specialize in guiding investors through the process. Remember, a lower DTI generally indicates a stronger financial position, which can lead to better loan terms and potentially a smoother investment journey.
When considering an investment property, your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a crucial factor. Lenders carefully evaluate your DTI to assess your ability to manage both your existing debt and the new mortgage. Companies like HPS Investment Partners , a global investment firm specializing in real estate, are often involved in these transactions. Understanding your DTI, and how it impacts your borrowing power, is essential for navigating the complex world of investment property financing.
When applying for a mortgage for an investment property, your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) plays a crucial role. Lenders assess your DTI to determine your ability to manage both your existing and new debt obligations. A good way to diversify your investment portfolio is by exploring options like unit investment trusts , which can offer exposure to a variety of assets.
While unit investment trusts might not directly impact your DTI, understanding your overall financial picture is key when making investment decisions, especially when it comes to purchasing an investment property.