Find the Best Place to Buy Investment Property

Finding the best place to buy investment property is a crucial step for any aspiring real estate investor. The right location can significantly impact your returns, while a poor choice can lead to losses and headaches. This guide explores key factors to consider when choosing a location, analyzing market trends, and understanding the different types of investment properties available. Whether you’re looking to purchase a single-family home, a multi-family unit, or commercial property, understanding the nuances of the market and the specific characteristics of each location is paramount to making a sound investment decision.
From understanding the local job market and population growth to analyzing infrastructure and property values, this comprehensive guide provides insights into the intricacies of real estate investment. We’ll delve into the importance of market research, financing options, and investment strategies, empowering you to make informed decisions that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Location: Best Place To Buy Investment Property
Location is arguably the most crucial factor in real estate investing. A well-chosen location can significantly boost your returns, while a poor choice can lead to financial losses. This section delves into key factors to consider when evaluating a location for your investment property.
Factors Contributing to a Good Investment Location
A good investment location typically possesses a combination of desirable features that attract residents, businesses, and capital. These factors create a strong foundation for property value appreciation and rental income generation.
- Job Market: A robust job market with diverse industries and high employment rates indicates a strong local economy. This translates to stable demand for housing and rental properties, as residents need a place to live while working.
- Population Growth: A growing population indicates a healthy demand for housing. As more people move to an area, the need for residential properties increases, driving up prices and rental rates.
- Infrastructure: Well-developed infrastructure, including transportation systems, schools, hospitals, and utilities, enhances a location’s livability and attractiveness.
- Amenities: The presence of desirable amenities, such as parks, recreational facilities, shopping centers, and cultural attractions, improves the quality of life for residents and can increase property values.
- Property Taxes: Lower property taxes can make a location more appealing to investors and homeowners, as it reduces their overall costs.
- Crime Rates: Lower crime rates create a safer environment for residents, which is a significant factor in property value and desirability.
Researching and Analyzing Location Factors
Thorough research is essential when evaluating potential investment locations. Here’s a breakdown of how to analyze key factors:
Job Market
- Unemployment Rate: Check the local unemployment rate to gauge the overall health of the job market. Lower unemployment rates generally indicate a strong economy.
- Major Employers: Identify major employers in the area and their industry sectors. A diverse range of industries reduces the risk of economic downturn due to reliance on a single sector.
- Job Growth Projections: Look for forecasts of future job growth in the area.
Population Growth
- Population Trends: Examine historical population growth trends and projections for future growth. This data can provide insights into the demand for housing.
- Demographics: Analyze the demographics of the area, including age distribution, household size, and income levels. This helps you understand the target market for your investment property.
Infrastructure
- Transportation: Evaluate the accessibility of public transportation, roads, and highways. Easy access to transportation options is crucial for residents’ daily commutes and overall convenience.
- Schools: Research the quality of schools in the area, as this can significantly impact property values and attract families.
- Hospitals: Assess the availability and quality of healthcare facilities. A strong healthcare infrastructure is important for residents’ well-being and can enhance a location’s desirability.
Types of Investment Properties

Choosing the right type of investment property is crucial for maximizing your returns and managing your risk. There are several types of properties available, each with its unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions about your investment strategy.
Single-Family Homes
Single-family homes are detached residences designed for a single family. They are popular among investors because of their relatively low entry cost and potential for appreciation.
- Pros:
- Lower entry cost compared to other property types.
- Potential for appreciation, especially in growing areas.
- Flexibility in terms of rental income and management.
- Can be used as a primary residence in the future.
- Cons:
- Limited rental income compared to multi-family properties.
- Higher risk of vacancy compared to multi-family properties.
- Requires more individual management and maintenance.
Multi-Family Units, Best place to buy investment property
Multi-family units, such as duplexes, triplexes, and apartment buildings, offer investors the opportunity to generate higher rental income with a single property.
- Pros:
- Higher potential rental income compared to single-family homes.
- Diversification of income streams with multiple tenants.
- Lower vacancy risk due to multiple units.
- Potential for economies of scale in management and maintenance.
- Cons:
- Higher initial investment cost compared to single-family homes.
- More complex management and maintenance requirements.
- Potential for tenant issues and conflicts.
Commercial Properties
Commercial properties, such as office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial warehouses, are designed for business operations. They offer investors the potential for higher returns but also come with greater risks.
- Pros:
- Potential for higher rental income and appreciation.
- Longer lease terms, providing more stable income.
- Potential for tax advantages and depreciation benefits.
- Cons:
- Higher initial investment cost and ongoing expenses.
- Greater risk of vacancy and tenant issues.
- Requires specialized knowledge and expertise in commercial real estate.
Land
Investing in land can be a long-term strategy, offering the potential for appreciation as demand for land increases.
- Pros:
- Potential for appreciation, especially in growing areas.
- Low maintenance costs compared to other property types.
- Flexibility in terms of future development or use.
- Cons:
- No immediate rental income or cash flow.
- Potential for long holding periods before appreciation.
- Requires careful due diligence to assess future development potential.
Comparison Table
| Property Type | Typical Returns | Associated Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Family Homes | 5-10% annual return | Vacancy, maintenance, tenant issues |
| Multi-Family Units | 8-15% annual return | Higher initial investment, tenant conflicts, management complexity |
| Commercial Properties | 10-20% annual return | High initial investment, vacancy, specialized expertise required |
| Land | Variable, depending on location and development potential | No immediate income, long holding periods, market volatility |
Market Research and Analysis

Market research is crucial for real estate investors because it helps identify lucrative opportunities and minimize risks. By understanding the current market conditions and future trends, investors can make informed decisions about where to invest, what type of property to buy, and how much to pay.
Analyzing Market Trends
Analyzing market trends involves examining various factors that influence property values and rental rates. This includes:
- Supply and Demand: Understanding the balance between available properties and the number of potential buyers or renters is essential. In a seller’s market, where demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. Conversely, in a buyer’s market, where supply outpaces demand, prices may decline.
- Property Values: Tracking historical property values and current trends can provide insights into the appreciation potential of a particular location. Factors such as economic growth, infrastructure improvements, and population growth can influence property values.
- Rental Rates: Analyzing rental rates in a given area helps determine the potential rental income from an investment property. Factors such as local job market, demographics, and rental demand influence rental rates.
Key Market Indicators
Here is a table outlining key market indicators and their potential impact on investment returns:
| Market Indicator | Potential Impact on Investment Returns |
|---|---|
| Population Growth | Higher population growth can lead to increased demand for housing, potentially driving up property values and rental rates. |
| Job Market Strength | A strong job market attracts residents, boosting demand for housing and potentially increasing property values. |
| Infrastructure Improvements | Investments in transportation, utilities, and other infrastructure can enhance the desirability of a location, potentially leading to higher property values. |
| Interest Rates | Lower interest rates make it cheaper to borrow money, which can stimulate demand for housing and potentially drive up prices. |
| Economic Growth | A robust economy can create a favorable environment for real estate investment, potentially leading to higher property values and rental rates. |
Financing Options
Securing financing is a crucial step in your investment property journey. Understanding the different financing options available can help you choose the best fit for your investment strategy and financial situation.
Mortgages
Mortgages are the most common type of financing for investment properties. They allow you to borrow a large sum of money from a lender, using the property as collateral.
- Conventional Mortgages: These are offered by banks and credit unions and typically require a down payment of 20% or more. Interest rates are usually lower than those on other types of loans, but you may need a good credit score to qualify.
- FHA Loans: Backed by the Federal Housing Administration, these loans require a lower down payment (as low as 3.5%) and may have more lenient credit requirements. However, they often come with higher interest rates and mortgage insurance premiums.
- VA Loans: Available to veterans, active-duty military personnel, and eligible surviving spouses, these loans often offer no down payment and lower interest rates. However, they have specific eligibility requirements.
Private Loans
Private loans, often called hard money loans, are typically offered by private lenders, such as individuals or investment firms. They are often used for short-term financing, particularly when traditional lenders are unwilling to provide a loan.
- Higher Interest Rates: Private loans usually have higher interest rates than conventional mortgages, reflecting the higher risk taken by the lender.
- Shorter Loan Terms: Private loans often have shorter loan terms, which can make them more expensive in the long run.
- Less Stringent Requirements: Private lenders often have less stringent credit requirements than traditional lenders, making them an option for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit.
Hard Money Loans
Hard money loans are a specific type of private loan often used for short-term financing in real estate investments. They are known for their quick funding and less stringent requirements, but they also come with higher interest rates and fees.
- Short-Term Financing: Hard money loans are typically used for short-term projects, such as flipping houses or bridging financing gaps.
- Higher Interest Rates: Hard money loans often have higher interest rates than conventional mortgages, reflecting the higher risk taken by the lender.
- Less Stringent Requirements: Hard money lenders often have less stringent credit requirements than traditional lenders, making them an option for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit.
Investment Strategies
Once you’ve identified a promising location and understand the types of properties available, it’s time to choose an investment strategy. Different strategies cater to different goals, risk tolerances, and time commitments.
Buy-and-Hold
This strategy involves purchasing a property and holding it for an extended period, typically years or even decades, to benefit from long-term appreciation and rental income.
- Appreciation: Real estate values generally increase over time, especially in growing areas. The appreciation in value can be substantial, especially over a long-term horizon.
- Rental Income: A buy-and-hold strategy generates passive income through rental payments. This income stream can offset expenses and contribute to your overall investment returns.
- Tax Benefits: Certain expenses related to rental properties, such as mortgage interest and property taxes, can be deducted from your taxable income, reducing your tax liability.
Risks
- Market Fluctuations: Real estate values can fluctuate, and a downturn in the market could result in temporary or even permanent losses.
- Property Management: Managing rental properties can be time-consuming and demanding, requiring knowledge of tenant screening, lease agreements, maintenance, and legal compliance.
- Vacancy Rates: There’s always a risk that your property might remain vacant for periods, leading to lost rental income.
Skills and Resources
- Financial Management: You’ll need to manage your finances effectively to cover mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, and maintenance expenses.
- Property Management Skills: If you’re not planning to hire a professional property manager, you’ll need to acquire skills in tenant screening, lease negotiations, rent collection, and property maintenance.
- Networking: Building a network of reliable contractors, real estate agents, and other professionals can be helpful for managing your property.
Fix-and-Flip
This strategy involves purchasing undervalued properties, renovating them, and then quickly reselling them for a profit.
- Potential for High Returns: Fix-and-flip projects can generate significant profits if done right. By acquiring properties below market value and adding value through renovations, you can increase their resale price considerably.
- Short-Term Investment: Fix-and-flip projects typically have a shorter holding period compared to buy-and-hold, allowing you to realize profits faster.
- Flexibility: You can choose to focus on specific types of properties and neighborhoods, allowing you to specialize in a particular market niche.
Risks
- Renovation Costs: Renovations can be expensive and unpredictable. Unexpected issues can arise, leading to cost overruns and delays.
- Market Timing: Selling a property quickly requires accurate market timing. If the market cools down or you overestimate the value of the renovated property, you may not be able to sell it for the desired price.
- Competition: The fix-and-flip market can be competitive, with other investors vying for the same properties.
Skills and Resources
- Renovation Expertise: You’ll need a good understanding of construction, renovation, and design principles. Alternatively, you’ll need to build a network of reliable contractors who can handle the work efficiently and cost-effectively.
- Project Management Skills: You’ll need to manage the renovation process effectively, ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Marketing and Sales Skills: You’ll need to market your renovated properties effectively to attract buyers and achieve a quick sale.
Rental Property Management
This strategy involves purchasing rental properties and hiring a professional property manager to handle all aspects of managing the property, including tenant screening, lease agreements, rent collection, and maintenance.
- Passive Income: Rental property management allows you to generate passive income from your investments without actively managing the properties yourself.
- Professional Expertise: Professional property managers have experience and expertise in managing rental properties, ensuring smooth operations and minimizing headaches.
- Time Savings: Delegating property management to professionals frees up your time to focus on other aspects of your life or business.
Risks
- Property Management Fees: You’ll need to pay property management fees, which can eat into your profits.
- Finding a Reliable Manager: Finding a trustworthy and experienced property manager is crucial. A poor choice can lead to problems with tenants, maintenance, and finances.
- Potential for Conflict: While professional managers can help, conflicts with tenants or issues with property maintenance can still arise, requiring your involvement.
Skills and Resources
- Financial Management: You’ll need to manage your finances effectively to cover mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, and property management fees.
- Networking: Building a network of reliable property managers and other real estate professionals can help you find the best options for managing your properties.
- Understanding of Leases and Rental Laws: While the property manager handles day-to-day operations, it’s still important to have a basic understanding of lease agreements and relevant rental laws.
Comparison of Investment Strategies
| Strategy | Typical Returns | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Buy-and-Hold | Moderate to High (Long-Term) | Investors seeking long-term growth, passive income, and tax benefits. |
| Fix-and-Flip | High (Short-Term) | Investors with renovation expertise, project management skills, and a tolerance for risk. |
| Rental Property Management | Moderate to High (Passive Income) | Investors seeking passive income and who are comfortable delegating property management responsibilities. |
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Investing in real estate involves navigating a complex web of legal and regulatory requirements. Understanding these aspects is crucial for a successful investment, as they can significantly impact your profitability and even lead to legal complications if not addressed properly. This section explores key legal and regulatory considerations that every real estate investor should be aware of.
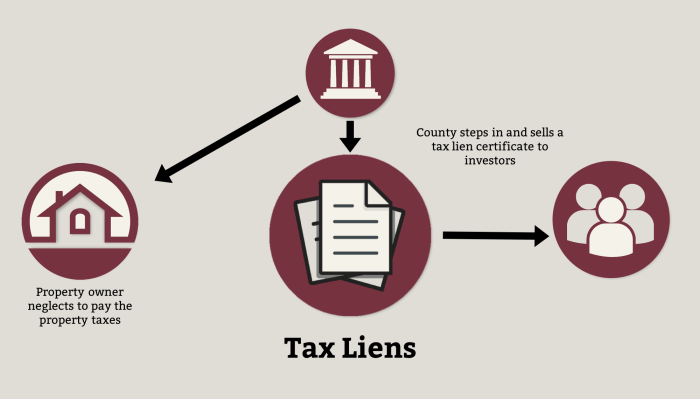
Property Taxes
Property taxes are levied by local governments on real estate owners. They are a significant recurring expense for property owners, and their rates can vary considerably depending on the location and type of property. Understanding property tax rates and how they are calculated is essential for budgeting and estimating your overall investment costs.
Property taxes are calculated based on the assessed value of your property, which is determined by the local government.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations are local laws that govern the use of land and properties within a specific area. They dictate what types of activities are permitted on a particular piece of land, such as residential, commercial, or industrial uses. Understanding zoning regulations is essential before purchasing a property, as it can limit your options for using or developing the property.
- Types of Zoning: Zoning regulations can be classified into various types, including residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural zoning.
- Zoning Violations: Violating zoning regulations can result in fines, legal action, or even the forced removal of structures.
Landlord-Tenant Laws
Landlord-tenant laws are designed to protect the rights and responsibilities of both landlords and tenants. These laws cover various aspects of the landlord-tenant relationship, including lease agreements, rent payments, security deposits, and eviction procedures. It is essential for landlords to familiarize themselves with these laws to ensure they are complying with all legal requirements.
- Lease Agreements: Lease agreements should clearly Artikel the terms and conditions of the rental agreement, including rent payments, security deposits, and the tenant’s responsibilities.
- Eviction Procedures: Landlords must follow specific legal procedures when evicting a tenant, which can vary depending on the jurisdiction.
Legal Process of Purchasing and Managing Investment Properties
The legal process involved in purchasing and managing investment properties can be complex and involves several steps.
- Due Diligence: Before purchasing a property, it is essential to conduct thorough due diligence, which involves reviewing the property’s title, conducting inspections, and researching any potential liens or encumbrances.
- Closing: The closing process involves signing all necessary legal documents, transferring ownership of the property, and disbursing funds.
- Property Management: Managing investment properties involves handling various tasks, such as collecting rent, maintaining the property, and addressing tenant issues.
Compliance with Local Laws and Regulations
Staying compliant with local laws and regulations is essential for avoiding legal issues and maintaining a positive reputation. This involves understanding and adhering to zoning regulations, building codes, property taxes, and landlord-tenant laws.
- Resources: Local government websites, real estate associations, and legal professionals can provide valuable resources and information on local laws and regulations.
- Consultations: Consulting with legal professionals, such as real estate attorneys, can provide guidance on navigating legal complexities and ensuring compliance.
Risk Management

Real estate investment, like any other venture, comes with inherent risks. Recognizing and managing these risks is crucial to maximizing returns and minimizing potential losses. Effective risk management involves identifying potential threats, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing strategies to mitigate or avoid them.
Potential Risks in Real Estate Investment
Potential risks in real estate investment can be categorized into various aspects, including market fluctuations, property-specific risks, and financial risks. Understanding these risks allows investors to develop informed strategies to manage them.
- Market Fluctuations: Real estate markets are cyclical, experiencing periods of growth and decline. Economic downturns, changes in interest rates, and shifts in demographics can influence property values and rental demand.
- Vacancy Rates: Vacant properties generate no income, impacting returns. High vacancy rates can be caused by factors like oversupply, economic recession, or a decline in local demand.
- Property Damage: Unforeseen events such as natural disasters, fires, or vandalism can lead to significant financial losses. Damage can require costly repairs, affecting rental income and potentially impacting property value.
- Interest Rate Changes: Fluctuations in interest rates can impact mortgage payments and borrowing costs, affecting the affordability of properties and influencing investment decisions.
- Property Management Issues: Ineffective property management can lead to decreased rental income, increased maintenance costs, and tenant disputes.
- Legal and Regulatory Changes: Changes in zoning laws, building codes, or tax regulations can impact property value and investment strategies.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
Mitigating risks in real estate investment involves taking proactive steps to reduce the likelihood and impact of potential threats. These strategies include:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different property types, locations, and market segments reduces the impact of any single risk.
- Thorough Due Diligence: Conducting extensive research on properties, neighborhoods, and market trends helps identify potential risks and inform investment decisions.
- Insurance: Obtaining appropriate insurance coverage, including property insurance, liability insurance, and rental income insurance, protects against financial losses from unforeseen events.
- Conservative Financing: Securing financing with a lower debt-to-equity ratio provides a financial buffer and reduces the risk of default.
- Professional Property Management: Hiring experienced property managers helps minimize vacancy rates, manage maintenance, and address tenant issues effectively.
- Staying Informed: Monitoring market trends, economic indicators, and regulatory changes helps anticipate potential risks and adjust investment strategies accordingly.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-life examples of successful real estate investments provide valuable insights into the strategies, challenges, and factors that contribute to positive outcomes. By examining these case studies, aspiring investors can gain practical knowledge and inspiration for their own ventures.
Successful Real Estate Investments
The success of real estate investments often hinges on strategic planning, thorough market research, and adaptability to changing market conditions. Here are a few examples of successful real estate investments:
- Flipping a Fixer-Upper: In a competitive market, an investor identified a distressed property in a desirable neighborhood. They purchased the property at a discount, invested in renovations, and subsequently sold it for a significant profit. This case study demonstrates the potential of identifying undervalued properties and adding value through improvements.
- Rental Property Portfolio: An investor strategically acquired a portfolio of rental properties in a growing city with a high demand for affordable housing. They focused on acquiring properties in areas with strong rental income potential and managed the properties effectively to maximize returns. This example showcases the benefits of diversifying investments and building a long-term rental income stream.
- Commercial Real Estate Development: A developer identified a prime location for a mixed-use commercial project. They secured financing, obtained necessary permits, and successfully developed a modern office building with retail space. This case study highlights the potential for significant returns from large-scale commercial real estate projects, but it also emphasizes the importance of careful planning and execution.
Challenges Faced by Investors
Real estate investment is not without its challenges. Investors often encounter obstacles that require resilience, adaptability, and strategic problem-solving. Some common challenges include:
- Market Fluctuations: Real estate markets are cyclical, and investors need to be prepared for periods of economic downturn or changes in market demand. This may involve adjusting investment strategies, delaying purchases, or holding onto properties during periods of market volatility.
- Unexpected Expenses: Unforeseen repairs, maintenance issues, or regulatory changes can lead to unexpected expenses. Investors should factor in a contingency fund to cover these potential costs and avoid financial strain.
- Tenant Issues: Dealing with challenging tenants, lease violations, or tenant turnover can be a significant challenge for rental property investors. Effective tenant screening, clear lease agreements, and proactive property management can mitigate these risks.
Factors Contributing to Successful Real Estate Investment
Several key factors contribute to the success of real estate investments. These include:
- Thorough Market Research: Understanding local market trends, demographics, and economic indicators is crucial for making informed investment decisions. This includes analyzing supply and demand, rental rates, property values, and future development plans.
- Financial Planning and Management: Investors need to carefully plan their finances, secure appropriate financing, and manage cash flow effectively. This includes budgeting for expenses, considering debt-to-equity ratios, and maintaining a healthy financial cushion.
- Strategic Investment Approach: Choosing the right investment strategy is essential. This involves considering risk tolerance, investment goals, and the long-term vision for the property. Investors should evaluate different investment options, such as buy-and-hold, flipping, or rental properties, based on their individual circumstances.
- Property Management: Effective property management is crucial for maximizing returns and minimizing risks. This involves handling tenant relations, maintaining the property, and collecting rent on time.
Investing in real estate can be a rewarding venture, but it’s crucial to approach it strategically. By carefully considering the factors discussed in this guide, you can increase your chances of success. Remember, the key to making smart investment decisions lies in thorough research, market analysis, and a well-defined investment plan. Armed with the right knowledge and tools, you can confidently navigate the real estate market and achieve your investment objectives.
Common Queries
What are some common mistakes to avoid when buying investment property?
Common mistakes include failing to conduct thorough due diligence, overlooking hidden costs, and not having a clear exit strategy. It’s crucial to research the property thoroughly, factor in all potential expenses, and plan for a potential sale or rental strategy.
How do I determine the right price to pay for an investment property?
Consider comparable properties in the area, recent sales data, and the potential rental income. Consult with a real estate professional or an appraiser for an objective assessment.
What are the tax implications of owning investment property?
Tax implications can vary depending on the type of property and your specific circumstances. Consult with a tax professional to understand the applicable taxes and deductions.
How can I find reliable tenants for my rental property?
Use reputable screening services, conduct thorough background checks, and clearly Artikel lease terms and expectations. Consider working with a property management company to handle tenant screening and property management.
The best place to buy investment property depends on your individual goals and financial situation. However, Dallas has been consistently ranked as a strong real estate market with high rental demand. If you’re looking for a promising location to invest in, check out dallas investment properties for sale for some great opportunities. Whether you’re searching for single-family homes, multi-family units, or commercial properties, Dallas offers a diverse range of options for investors of all levels.
The best place to buy an investment property depends on your individual goals and financial situation. If you’re looking for a strong market with potential for growth, consider investment properties in Maryland. This state offers a diverse range of options, from bustling cities to charming suburbs, providing opportunities for both long-term appreciation and consistent rental income. Ultimately, the best place to buy an investment property is where you can find the right balance of risk, reward, and personal preferences.
Finding the best place to buy investment property depends on many factors, including your budget, investment goals, and the local market. One way to make a down payment more manageable is to explore a 10 down investment property loan , which can open up more opportunities in areas with higher property values. Ultimately, the best place to buy will be the one that aligns with your individual financial situation and investment strategy.