Are Tax Liens a Good Investment? Exploring the Potential
Are tax liens a good investment? This question sparks curiosity among those seeking alternative real estate investment opportunities. Tax liens represent a unique avenue for investors to potentially capitalize on delinquent property taxes, offering the chance for high returns and short-term gains. However, navigating this complex world requires a deep understanding of the risks, legal intricacies, and due diligence necessary to make informed decisions.
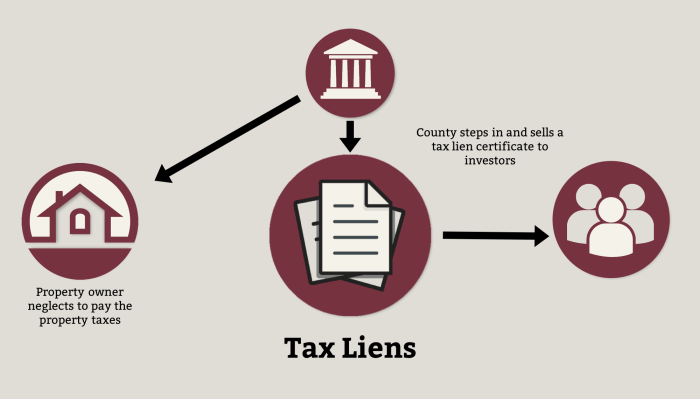
Tax liens arise when property owners fail to pay their property taxes, prompting the government to place a lien on the property. These liens can be purchased by investors at tax sales, allowing them to acquire a claim on the property. While the potential for high returns is enticing, investors must be prepared for the complexities of the process, including the possibility of default, legal challenges, and the need for thorough research.
Understanding Tax Liens
A tax lien is a legal claim placed on a property by a government entity, typically a state, county, or municipality, to secure the payment of unpaid taxes. When an individual or business fails to pay their taxes, the government has the right to place a lien on their property, including real estate, vehicles, or other assets. This lien gives the government a legal right to seize and sell the property to recover the unpaid taxes.
Types of Tax Liens
Tax liens can be categorized based on the level of government that imposes them. The most common types include:
- Federal Tax Liens: These liens arise from unpaid federal taxes, such as income tax, corporate tax, or payroll tax. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has the authority to file federal tax liens.
- State Tax Liens: These liens are imposed by state governments for unpaid state taxes, such as sales tax, income tax, or property tax. State revenue agencies typically handle the filing of state tax liens.
- Local Tax Liens: These liens are placed by local governments, such as cities or counties, for unpaid property taxes or other local taxes. The local tax assessor or collector’s office is responsible for filing local tax liens.
Situations Where a Tax Lien Might Be Placed
Tax liens can be placed on a property in various situations, including:
- Unpaid Property Taxes: The most common reason for a tax lien is the failure to pay property taxes. This can happen if the property owner neglects to pay their taxes, faces financial difficulties, or simply forgets to pay.
- Unpaid Income Taxes: Individuals and businesses that fail to pay their income taxes can also face tax liens. The IRS may file a lien on their property to secure payment of the unpaid taxes.
- Unpaid Sales Taxes: Businesses that fail to collect and remit sales tax to the state can be subject to tax liens. The state revenue agency may file a lien on the business’s property to recover the unpaid sales tax.
- Unpaid Business Taxes: Corporations and other businesses may also face tax liens for unpaid corporate taxes, payroll taxes, or other business-related taxes.
Tax Liens as Investments

Tax liens can be an intriguing investment option for those seeking high returns and short-term holding periods. These liens represent a claim on a property that’s secured by unpaid taxes, allowing investors to potentially earn significant profits by purchasing them at a discount and then collecting the full amount owed plus interest. However, like any investment, tax liens come with their own set of risks and complexities.
Potential Benefits of Investing in Tax Liens
Investing in tax liens can potentially offer attractive returns, especially in comparison to traditional investments like stocks or bonds. The primary benefit lies in the opportunity to earn a high rate of interest on the investment. Tax liens typically carry interest rates that are significantly higher than those offered by traditional savings accounts or bonds. This high interest rate can translate into substantial profits for investors, especially if they can purchase the liens at a discount. Additionally, tax liens are often considered relatively short-term investments. Depending on the jurisdiction, investors can potentially recoup their investment and earn a profit within a few months or a year. This short-term nature of tax lien investments allows for quick returns and the ability to reinvest funds more rapidly.
Risks Associated with Tax Lien Investments, Are tax liens a good investment
While tax liens offer the potential for high returns, they also come with inherent risks that investors need to carefully consider.
- One major risk is the possibility of default. If the property owner fails to pay the back taxes, the investor may have to go through the foreclosure process to recover their investment. This process can be lengthy, expensive, and ultimately unsuccessful, potentially resulting in a complete loss of the investment.
- Another significant risk is the complexity of the tax lien process. Understanding the specific laws and regulations governing tax liens in each jurisdiction can be challenging. Investors need to navigate the legal intricacies, including proper documentation, bidding procedures, and foreclosure processes. Mistakes or oversights can lead to legal complications and financial losses.
- Additionally, investors need to consider the potential for hidden problems with the property. Even though the lien is secured by the property, there is no guarantee that the property is in good condition or free from encumbrances. Hidden defects, liens, or legal issues can significantly impact the value of the property and potentially lead to financial losses for the investor.
Comparing Tax Lien Investments to Other Real Estate Options
Tax lien investments can be compared to other real estate investment options, such as foreclosures or traditional rentals.
- Foreclosures, like tax liens, involve acquiring properties that are in default. However, foreclosures typically involve a longer and more complex process. While foreclosures offer the potential for greater profit due to lower purchase prices, they also carry higher risks and require greater capital investment.
- Traditional rentals offer a more stable and predictable income stream. However, rental properties require significant upfront capital investment, ongoing maintenance costs, and tenant management responsibilities. While rental properties can provide long-term returns, they often involve lower returns than tax liens or foreclosures.
Due Diligence and Research

Thorough due diligence is crucial when considering tax liens as investments. It involves evaluating the property’s value, understanding the legal complexities, and assessing the potential risks and rewards.
Examining Public Records and Property Condition
Before investing in a tax lien, it is essential to examine public records and assess the property’s condition. This process helps you understand the property’s history, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions.
- Property Records: Review the property’s deed, tax records, and any existing liens or encumbrances. This information can reveal details about the property’s ownership, outstanding taxes, and any legal challenges. For example, a property with multiple liens might indicate financial distress or potential legal complications.
- Property Condition: Conduct a physical inspection of the property to assess its condition. This involves examining the structure, utilities, and any potential repairs or renovations needed. For instance, a dilapidated property might require significant investment to make it habitable, impacting your potential return.
Determining Fair Market Value and Estimating Potential Profits
Accurately assessing the fair market value of a property with a tax lien is essential for estimating potential profits. This involves considering various factors and using reliable valuation methods.
- Comparable Sales: Analyze recent sales of similar properties in the area to establish a benchmark for the property’s value. This method helps you understand the current market conditions and the potential selling price. For instance, if comparable properties in the neighborhood have sold for $200,000, it might be reasonable to assume that the property with a tax lien could fetch a similar price.
- Property Appraisal: Consider obtaining a professional appraisal to determine the property’s fair market value. This provides an independent assessment of the property’s worth, ensuring that your investment decisions are based on accurate information.
- Potential Profits: Once you have determined the fair market value, you can estimate your potential profits. Subtract the purchase price of the tax lien, any legal fees, and potential renovation costs from the estimated selling price. For example, if you purchase a tax lien for $10,000, the property’s estimated value is $150,000, and you anticipate $10,000 in renovation costs, your potential profit would be $140,000.
Understanding the Legal Process and the Rights of the Property Owner
Tax liens are governed by specific legal processes, and it is crucial to understand these processes and the rights of the property owner. This knowledge helps you navigate the legal complexities and protect your investment.
- Redemption Period: The property owner typically has a redemption period to pay the back taxes and reclaim ownership of the property. You need to be aware of the redemption period and its implications for your investment. For example, if the property owner redeems the property within the redemption period, you might lose your investment.
- Foreclosure Process: If the property owner fails to redeem the property, you can initiate foreclosure proceedings to acquire ownership. Understanding the foreclosure process, including the required legal steps and timelines, is crucial. For instance, you might need to file a lawsuit to obtain a court order for the property’s sale.
- Property Owner’s Rights: Even with a tax lien, the property owner still retains certain rights. You must respect these rights and adhere to the legal requirements throughout the process. For example, you might need to provide the property owner with notice before initiating foreclosure proceedings.
Purchasing and Managing Tax Liens: Are Tax Liens A Good Investment
Once you’ve identified potential tax liens and conducted thorough due diligence, you’re ready to make an offer and potentially purchase the lien. This process involves navigating tax sales, understanding different lien certificates, and effectively managing your investment.
Tax Lien Purchase Process
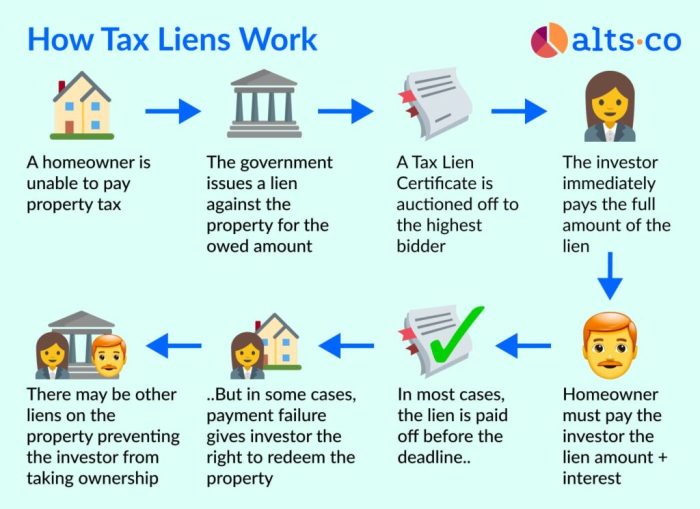
Purchasing a tax lien typically involves participating in a tax sale, where properties with unpaid taxes are auctioned off to the highest bidder. This process can vary depending on the state and jurisdiction. Here’s a general overview:
- Register for the Tax Sale: Contact the relevant government agency or tax collector to obtain information about upcoming tax sales and registration requirements. This usually involves providing personal information and paying a registration fee.
- Review Tax Sale Listings: Before the sale, review the list of properties available. This information often includes the property address, the amount of unpaid taxes, and any existing liens. You can use this information to assess the potential return on investment.
- Attend the Tax Sale: Arrive at the tax sale on the designated date and time. The sale usually takes place in a public setting, like a courthouse or government building.
- Bid on Tax Liens: When the property you’re interested in is brought up for auction, you can submit bids. The bids are typically made in increments of a specified amount. The highest bidder wins the tax lien.
- Secure the Tax Lien Certificate: After winning the bid, you’ll receive a tax lien certificate, which officially documents your ownership of the lien. This certificate Artikels the terms of the lien, including the amount owed, the interest rate, and the redemption period.
- Pay the Purchase Price: You’ll need to pay the winning bid amount to the tax collector within a specific timeframe, usually within a few days of the sale.
Tax Lien Certificates
Tax lien certificates come in different types, each with its own set of terms and conditions. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Here’s a breakdown of common types:
- Regular Tax Lien Certificate: This is the most common type of certificate. It grants you the right to collect the unpaid taxes, plus interest and penalties, from the property owner. You’ll typically receive a specified interest rate on your investment, which varies depending on the state.
- Tax Deed Certificate: This type of certificate gives you the right to acquire ownership of the property after a certain period if the property owner fails to redeem the lien. The redemption period varies by state, but it’s typically between one and three years.
- Deferred Payment Certificate: This certificate allows you to pay for the tax lien in installments, rather than paying the full amount upfront. This option can be beneficial if you have limited funds available. However, it may come with higher interest rates.
Managing Tax Liens
After acquiring a tax lien, you need to actively manage it to maximize your return on investment. This involves collecting payments from the property owner and potentially enforcing the lien if they fail to redeem it.
- Contact the Property Owner: Once you purchase the lien, reach out to the property owner to inform them of your ownership and the terms of the lien. You’ll need to provide them with instructions on how to redeem the lien by paying the outstanding taxes, interest, and penalties.
- Collect Payments: If the property owner decides to redeem the lien, they’ll make payments to you according to the terms of the certificate. It’s important to keep accurate records of all payments received.
- Enforce the Lien: If the property owner fails to redeem the lien within the redemption period, you can take steps to enforce it. This process typically involves filing a lawsuit to obtain a tax deed, which gives you ownership of the property.
Tax Lien Investment Strategies
Tax lien investing offers a variety of strategies that can cater to different risk tolerances and investment goals. Understanding these strategies and their nuances is crucial for maximizing returns and mitigating potential risks.
Buy and Hold Strategy
The buy and hold strategy involves purchasing a tax lien and holding it until the property owner redeems it or the lien matures. This strategy is often favored by investors seeking a steady stream of income from the interest earned on the lien.
The interest rate on a tax lien is typically fixed and can range from 10% to 20% or more, depending on the state and the specific lien.
Investors can choose to hold the lien for the full term, typically a few years, or sell it to another investor before maturity. The decision to hold or sell depends on factors such as the expected future interest rates, the likelihood of redemption, and the investor’s overall investment goals.
Flipping Tax Liens
Flipping tax liens involves purchasing a tax lien and quickly reselling it to another investor for a profit. This strategy relies on finding undervalued liens and taking advantage of market inefficiencies.
Flipping tax liens can be more risky than buy and hold strategies, as it involves finding buyers and timing the market correctly.
However, it can also offer higher potential returns if done successfully. Factors that can contribute to successful flipping include:
- Knowledge of the local market and the value of properties.
- Ability to identify undervalued liens with high redemption potential.
- Effective marketing and negotiation skills to attract buyers.
Tax Lien Investment Strategies in Different Market Conditions
Market conditions and economic trends can significantly impact the success of tax lien investments.
- In a strong economy, property values tend to rise, increasing the likelihood of redemption. This can benefit both buy and hold and flipping strategies.
- During economic downturns, property values may decline, making it more difficult for property owners to redeem their liens. This can increase the risk of foreclosure and reduce the potential returns for investors.
- Interest rate fluctuations can also impact tax lien investments. When interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing money increases, which can make it more expensive for property owners to redeem their liens. This can lead to higher returns for investors.
Investing in tax liens can be a lucrative strategy for those seeking high returns and short-term opportunities in the real estate market. However, it’s crucial to approach this investment with caution, conducting thorough research, understanding the risks, and adhering to legal guidelines. By carefully considering the potential benefits and challenges, investors can make informed decisions and potentially reap the rewards of this unique investment avenue.
FAQ Corner
How much do tax liens typically cost?
The cost of a tax lien varies depending on factors like the property’s value, the amount of delinquent taxes, and the location. Generally, you’ll need to bid at a tax sale to acquire a lien, and the winning bid often reflects the outstanding taxes plus interest and penalties.
What are the legal implications of purchasing a tax lien?
Purchasing a tax lien grants you a legal claim on the property, but it doesn’t automatically give you ownership. The property owner still has the right to redeem the property by paying off the delinquent taxes and any accrued interest. It’s essential to understand the legal process and the rights of the property owner before investing.
Are there any tax benefits associated with tax lien investments?
While tax liens themselves aren’t tax deductible, you may be able to claim deductions related to expenses incurred in managing the lien, such as legal fees or property maintenance costs. It’s recommended to consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.
While tax liens can offer potential returns, they come with risks. If you’re new to real estate investing, consider starting with a more traditional approach like buying your first investment property. This allows you to gain experience and build a portfolio before tackling the complexities of tax lien investments.
While tax liens can offer an intriguing investment opportunity, they require careful research and due diligence. If you’re considering a more traditional investment, investing in resort properties could be an attractive option. However, both strategies carry their own set of risks and rewards, and it’s essential to weigh them carefully before making any investment decisions.
Tax liens can be a risky yet potentially rewarding investment, offering the chance to acquire property at a discount. One strategy to consider, especially if you’re focusing on long-term appreciation, is an investment property interest only mortgage. This allows you to pay only the interest on your loan, freeing up cash flow for other investments, including those like tax liens.
While tax liens can be a viable option, it’s crucial to thoroughly research and understand the associated risks and legal complexities before diving in.








