Sitemap Index.xml

Sitemap Index.xml: The Key to Mastering Website Navigation
In the vast and ever-expanding world of websites and digital content creation, the term “Sitemap Index.xml” might not immediately spark a rush of excitement or recognition for everyone. Yet, it holds major significance behind the curtains of website optimization and search engine recognition. At its core, a sitemap index is akin to a roadmap for search engines, guiding them through the complex corridors of data nestled within a website. In our digital age—where presence on the web equates to influence and reach—a sitemap index is less a mere convenience and more of a necessity for ensuring your digital footprint is not only identified but prioritized by search engines.
Imagine for a moment stepping into an enormous library, shelves brimming with a multitude of books, some on bestseller lists, others hidden away in dusty corners. Without a systematic catalog, finding a specific book is a daunting task, akin to finding a needle in a haystack. Similarly, a sitemap acts as that critical catalog in the digital realm—systematically listing, categorizing, and ensuring each page of your website is indexed and easily discoverable by search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo.
But what exactly is a Sitemap Index.xml? At first glance, you might visualize a series of files containing a list of references to other XML sitemap files. While partially true, to delve deeper into its functionality and importance, one must embrace its role as the maestro orchestrating the symphony of XML sitemap files within complex websites. For sites sprawling over numerous pages, be it e-commerce giants with extensive product catalogs, media outlets with countless articles, or educational institutions offering diverse courses—a single sitemap might resemble a tangled web. This is where the asset of a sitemap index manifests, neatly segmenting and organizing these sitemap files for effortless interpretation.
For webmasters, SEO experts, and even digital marketers, leveraging a sitemap index can unlock multitudinous benefits, from enhancing crawl efficiency to optimizing search engine rankings. However, the beauty of a sitemap index lies not just in its grand service to search engines, but also in how it potentially improves a site’s internal navigation, enriching user experience in the process. As you imagine the roles interwoven by this unassuming file, it becomes evident that a sitemap index is not just a file—it’s an essential framework integral to the operational success of a modern website.
Wondering about the crafting process? Creating a sitemap index demands a meticulous approach, focusing on critical elements like frequency of updates, priority, and ensuring none of the search bots hits a dead end. This digital architecture’s effectiveness hinges on its adherence to the protocols outlined by search engines, where even slight missteps can result in critical parts of a website being overlooked. Comprehensive tools and insights can be employed to generate these XML files, making this endeavor less meticulous and more strategic.
Our exploration of Sitemap Index.xml will delve into several pivotal themes: how to navigate the creation and submission processes to search engines, discerning the technical requirements mandatory for optimal functionality, and sharing actionable insights to elevate your site’s performance. We will also spotlight some of the industry’s best practices and contemporary tools available for webmasters aiming to maximize their technological acumen without getting lost in intricate technicalities.
Knowledge about Sitemap Index.xml is not confined solely to the realm of IT specialists or web developers. Its understanding bears infinite value on an expansive spectrum, including small business proprietors seeking to augment their online visibility, writers aiming to amplify their portfolio’s reach, and entrepreneurs navigating digital branding landscapes. Through strategic deployment of well-structured sitemaps and index files, anyone can level the playing field in the competitive domain of online presence.
As we embark on this journey into the depth and breadth of Sitemap Index.xml, prepare to transform mundane web jargon into actionable strategies. Whether you are an industry veteran honing your skill set, a digital newcomer eager to learn, or simply a curious mind intrigued by the synchronization of technology and functionality, this guide is tailored for you. Join us as we unravel the complexities of digital sitemaps, and discover how they can accelerate your path to becoming a web navigation virtuoso.
In the sections that follow, you will find a treasure trove of insights and resources unpacking everything from the basics of XML sitemaps to advanced strategies for managing sitemap indices. With this knowledge, you can deftly navigate the digital landscape, enhance your website’s discoverability, and ultimately, command a more prominent presence in the bustling world of online content.
Understanding Sitemap Index.xml
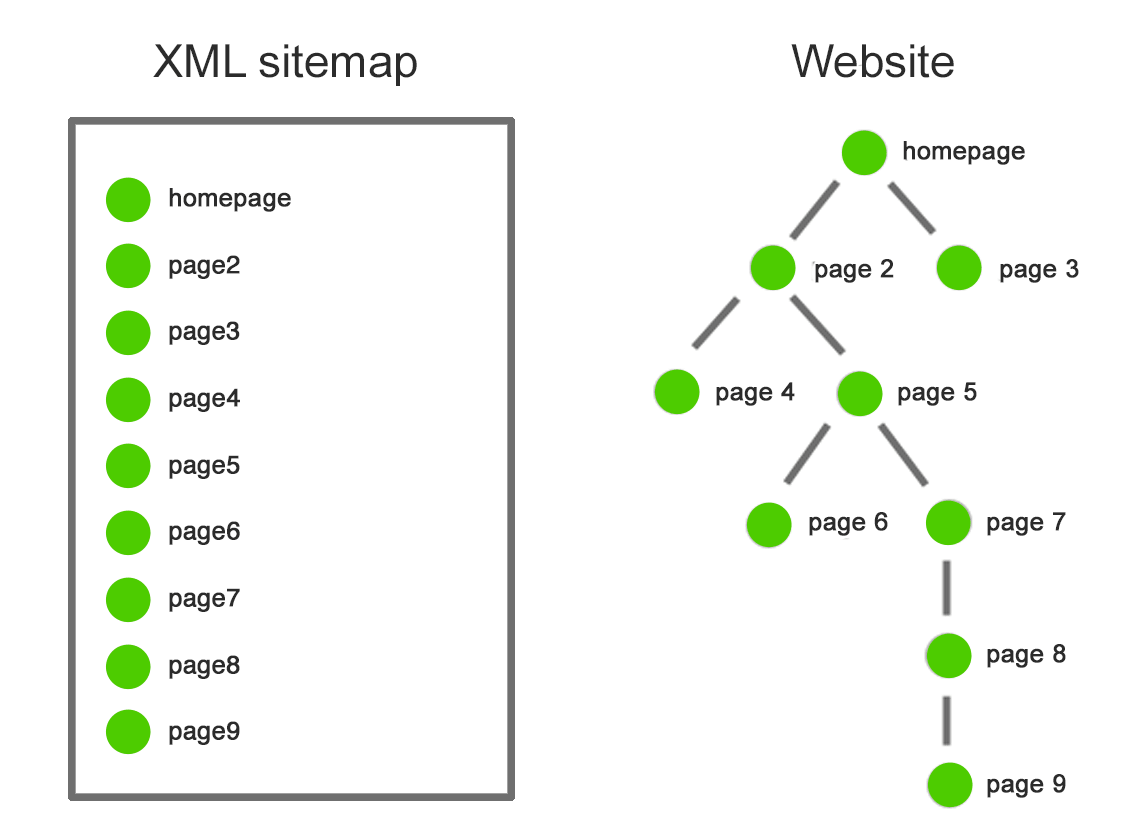
A Sitemap Index.xml is essentially a file that references other sitemap files, organizing them effectively for search engines. This is particularly useful for larger websites with a multitude of sitemaps. While a regular sitemap lists out the individual URLs of your website, a sitemap index does the same for multiple sitemaps. This hierarchy ensures that search engines can crawl your site more efficiently.
Why You Need a Sitemap Index
For websites with numerous URLs, a single sitemap may exceed the 50MB or 50,000 URL limit imposed by search engines. In these instances, dividing your URLs into multiple sitemaps and organizing them with a sitemap index is advisable. Not only does this adhere to search engine guidelines, but it also aids in optimal website indexing and ranking. Moreover, a sitemap index allows for better categorization and prioritization of your site’s content.
- Efficient Crawling: Ensures search engines find all pages of your site.
- Scalability: Easily manage large websites with multiple sections.
- Better Organization: Segregate URLs based on content type or priority.
Crafting Your Sitemap Index.xml: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Plan Your Sub-Sitemaps
Begin by determining the structure and the number of sub-sitemaps you’ll need. Categorize your website’s pages based on content type, priority, or update frequency. For instance, if the website hosts a blog, an e-commerce section, and a static page section, consider creating separate sitemaps for each type.
Step 2: Generate Individual Sitemaps
Once you’ve determined how to segment your URLs, the next step is generating each sitemap. This can be accomplished using various online tools, CMS plugins, or even programmatically through scripts. Ensure each sitemap adheres to the XML protocol, listing URLs along with optional metadata such as lastmod, changefreq, and priority.
Step 3: Construct the Sitemap Index.xml
With your individual sitemaps ready, you can now create the index file. The Sitemap Index.xml should begin with the XML header and a <sitemapindex> tag, which contains multiple <sitemap> entries. Each entry points to a specific sitemap and must include:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<sitemapindex xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<sitemap>
<loc>http://example.com/sitemap_blog.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2023-10-01</lastmod>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>http://example.com/sitemap_shop.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2023-10-02</lastmod>
</sitemap>
</sitemapindex>
Step 4: Validate Your Sitemap Index.xml
Before implementing your sitemap index, ensure it is error-free by validating it through an XML validator. This step is crucial to avoid any crawling issues with search engines. Many online validators can help identify syntax errors or structural problems in your sitemap index.
Step 5: Submit Your Sitemap Index to Search Engines
With a validated sitemap index, the next step is submitting it to search engines to facilitate efficient crawling. For Google, use the Google Search Console; for Bing, utilize Bing Webmaster Tools. Regularly check these platforms for any errors and update your sitemaps as necessary to reflect content changes on your site.
Best Practices for Maintaining Your Sitemap Index
Keep the following best practices in mind to ensure your sitemap index remains effective:
- Update Regularly: Review and update your sitemap index whenever major changes are made to your site’s structure or content.
- Check for Errors: Use webmaster tools to regularly check for sitemap errors that could hinder site crawling.
- Organize Thoughtfully: Strategically categorize URLs in your sitemaps to optimize search engine understanding and indexing.
- Monitor Server Resources: Ensure that your server can handle the sitemap requests efficiently without affecting site performance.
By following these steps and maintaining best practices, you’ll craft a well-structured sitemap index that enhances your site’s SEO and ensures efficient search engine crawling.
Concluding Your Sitemap Index Journey: Key Takeaways
As we draw this informative journey on Sitemap Index.xml to a close, it’s vital to reflect on the core insights and actionable strategies we’ve gained. Thanks to your keen interest and understanding, you’re now equipped to leverage sitemaps as a critical component of your website’s SEO arsenal, ensuring your content is effectively crawled and indexed by search engines.
Understanding the Sitemap Index
The journey began with an exploration of what a Sitemap Index.xml is and its fundamental purpose. We discussed how a Sitemap Index is a file that lists several sitemaps and plays a pivotal role in structuring your website’s indexing mechanisms. This allows search engines to systematically access and understand your website’s architecture more efficiently. This crucial understanding underscores the importance of a Sitemap Index as a gateway to improved search visibility.
The Importance of Proper Sitemap Index Configuration
One key takeaway is the technical knowledge required to successfully configure your Sitemap Index. We delved into best practices for organizing and categorizing sitemaps within the index. Correct configuration not only enhances crawl efficiency but also minimizes the likelihood of crawling errors. By taking a systematic approach to indexing your sitemaps, you’ve laid a solid foundation for robust SEO practices.
Adhering to Search Engine Guidelines
It is essential to align your Sitemap Index.xml with the guidelines issued by major search engines like Google. Throughout the article, we stressed the importance of compliance with the latest protocols and standards that govern XML sitemaps. Regularly updating and validating your Sitemap Index ensures that it remains an accurate reflection of your website’s structure, thus improving content discoverability.
The Role of Automation and Tools
In our exploration, we highlighted how automation tools and platforms can significantly simplify the creation and maintenance of your Sitemap Index. We evaluated a variety of tools, from WordPress plugins to third-party services, which help in effortlessly generating sitemap indexes and keeping them up-to-date. Leveraging these tools can save time and reduce the complexity involved in managing extensive web architectures.
Monitoring and Analytics
Monitoring your Sitemap Index’s performance was another vital aspect we covered. Using analytics tools like Google Search Console to track sitemap submission statistics and indexing status can provide valuable insights into the health of your sitemaps. These insights facilitate ongoing optimizations and ensure errors are promptly addressed, keeping your website’s SEO performance on a strong trajectory.
Strategic Use of Sitemap Index in SEO
Understanding and strategically using your Sitemap Index can amplify your SEO efforts, improving your site’s overall visibility and usability. We discussed various strategies, such as leveraging priority and change frequency tags within sitemaps, to communicate to search engines which parts of your site are most important and should be crawled more frequently. Such strategic implementations can considerably influence how search engines perceive and rank your content.
Looking Ahead: Continuous Improvement
Wrapping up your Sitemap Index journey is not the end; it is, instead, the foundation for continuous improvement. The dynamic nature of the web means that your Sitemap Index should be a living document, regularly updated to reflect new content and site structure changes. Through vigilance and adaptability, you ensure that your SEO efforts remain effective, no matter how your site evolves.
Your Call to Action
As we conclude, I invite you to take these learnings and apply them to your own digital endeavors. Whether you’re tweaking an existing Sitemap Index or creating one anew, the knowledge gained here is your roadmap to enhancing your website’s SEO footprint.
- Explore additional tools and resources that can automate and streamline your sitemap management process.
- Engage with communities or forums focused on SEO to stay updated on new developments and share your experiences.
- Conduct regular sitemap audits to ensure that your index remains accurate and aligns with your website’s ongoing modifications.
The world of SEO is ever-changing, and with your newfound expertise, you are well-prepared to navigate its complexities. Remember, a well-organized Sitemap Index is not just a technical necessity; it’s a powerful tool to aid in achieving your broader digital goals. Stay curious, keep learning, and embrace the continuous improvement of your digital footprint.
Thank you for joining me on this exploration of Sitemap Index.xml. If you found this guide helpful, consider sharing it with others who might benefit as well. Let’s continue enhancing the digital web, one sitemap at a time!
Happy indexing!











 News
News Review
Review Startup
Startup Strategy
Strategy Technology
Technology
